Multiple
Choice Question (MCQ): 1 mark each
1. Which force is applied between the sun and the earth?
a) Gravitational force b) Gravity c) Electronic force d) Magnetic force
2. What is the value of Gravitational constant?
a) 6×10-11 Nm2Kg-2 b) 6.67×10-11
Nm2Kg-2
c) 9.8×10-11
Nm2Kg-2 d)
9.97×10-11 Nm2Kg-2
3. What is the gravitational force acting between A and
B?
a) 1N b) 9.8 N c) 6.67×10-11N d) 6.67×1011N
4. When the mass of two body is halved keeping the
distance constant, the gravitational force between them is …………..
a)
5. What is the average acceleration due to gravity on
Jupiter?
a) 9.78m/s2 b) 1.67 m/s2 c) 2.5 m/s2 d) 25m/s2
6. What is the value of gravitational constant on the
surface of moon?
a) 1.67 m/s2 b) 6.67 m/s2 c) 6.67×10-11Nm2kg-2 d) 9.8 m/s2
7. How many dynes are equal to 1 Newton?
a) 100 dynes b) 1000 dynes c) 10000 d) 100000
8. Where is the value of acceleration due to gravity
zero?
a) at the center b) at the equator c) at the poles d) at the Mt. Everest
9. What is the mass of a person of 60Kg on the surface of
moon?
a) 60 kg b)
100.2 KG c) 588N d) 600 N
10. How
Answers:
1(a), 2(b), 3(c), 4(c), 5(d), 6(c), 7(d), 8(a), 9(a)
Very
Short Answer type Questions: [1 mark Each]
1. What do you mean by gravitational constant 'G'?
Gravitational constant is the force of gravitation between two
bodies each with a mass of one kilogram at a distance of 1 meter apart. It is
also called Astronomical constant or Universal gravitational constant.
2.
Write
the SI unit and Value of gravitational constant.
The SI unit of gravitational constant 'G' is Nm2/kg2 and value of 'G' is 6.67x 10-11 Nm2/ kg2.
3.
What
is acceleration due to gravity?
The acceleration produced in a freely falling body without any
resisistance towards the surface of the earth as a result of the gravity is
called acceleration due to gravity.
4.
What
is free fall?
The free fall is defined as the fall of an object with the
velocity of the acceleration due to gravity without an external
resistance.
5.
Define
the gravitation.
Gravitational force is the force of attraction produced between
any two object by virtue of their masses. Everybody in this universe attracts
another body towards itself. The mutual forces of attraction between any two
bodies is known as force of gravitation.
6.
State
Newton's law of gravitation.
Newton's universal law of gravitation states that "The
gravitational force produced between any two bodies is directly proportional to
the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the
distance between their centers."
7.
The
value of universal gravitational constant is 6.67×10-11Nm2/kg2. What does it mean?
The value of universal gravitational constant is 6.67×10-11Nm2/kg2, it means that the
gravitational force between two bodies of 1kg masses placed at a distance of 1m
is 6.67×10-11N.
8.
What
is weightlessness?
Weightlessness is the condition of a body when it is completely loses
its weight and become weightless.
9.
In
which condition will acceleration due to gravity on parachute be zero?
Acceleration due to gravity on parachute becomes zero when the
force of gravity and the upthrust due to air is equal and opposite to each other.
10.
Write
the relationship between mass of a body and weight in terms of formula.
The relationship between mass of a body and weight in terms of
formula is:
W=GMm/R2
Where,
W = weight of the body, G= Gravitational constant, M = Mass of the
earth, m= mass of object and R = Radius of the earth.
11.
In
which direction does the force of gravity act?
The force of gravity acts towards the centre of the earth.
12.
Write
one effect seen on ocean or sea due to gravitation of the moon and the sun?
Tides are formed on sea and ocean due to the gravitation of the
moon and the sun.
13.
Where
does the weight of a body maximum on the surface of the earth?
Weight of the body is maximum on the poles of the earth.
14.
What
are the two factors that affect the forces of gravitation?
Two factors that affect the force of gravitation are: Masses of
the two bodies and the distance between them from their centres.
15.
What
is the value of acceleration due to gravity at equatorial region of the earth?
Write its SI unit.
The value of acceleration due to gravity at equatorial region of
the earth is 9.78 m/s2. It SI unit is m/s2.
16.
1.
Astronaut
feel weightlessness in spacecraft, why?
Inside the spacecraft, the gravitational force of attraction on
him is balanced by the centrifugal force of the spacecraft. So the net force
acting on him is zero. Hence in this condition astonaut inside the spacecraft
feels weightlessness.
2.
A
large stone of 20 kg and small stone of 5 kg are dropped simultaneously from
certain height. Which one reaches on the ground first? Why?
Both the large stone of 20 kg and small stone of 5 kg mass will
drop simultaneously on the surface. This is because acceleration due to gravity
is independent of the mass of the body and the value of acceleration due to
gravity is equal on both the stones.
3.
What
happens to the weight of an object when it is taken from the earth to the moon,
why?
Weight of a body is directly proportional to the acceleration due
to gravity. The value of acceleration due to gravity is 6 times lesser on the
moon than that on the earth. So the weight of an object decreases by 6 times on
the moon than on the earth.
4.
The
acceleration due to gravity on the surface of Jupiter is 25m/s2. What does it mean?
The acceleration due to gravity on the Jupiter is 25m/s2. It means that the velocity of a freely falling body towards the
surface of Jupiter increases at the rate of 25m/s in every second.
5.
Write
the reason behind the atmosphere does not escape away from the earth.
The atmosphere does not escape away from the earth because the
gravity of the earth binds the atmosphere and prevent it from being escape into
the space.
6.
Write
any two differences between gravity and acceleration due to gravity.
7.
Two differences between
gravity and acceleration due to gravity are:
|
Gravity |
Acceleration due to gravity |
|
1. Gravity is the
force with which the earth or havenly body pulls an object towards its
center. |
1. Acceleration due to
gravity is the acceleration produced in a freely falling body due to the
gravity of the earth. |
|
Its SI unit is Newton |
Its SI unit is m/s2. |
Why an iron ball and a feather fall together in a vacuum?
8.
All freely falling
bodies fall with the same acceleration of 9.8m/s2. In vacuum there is no
resistance, so an iron ball and a feather travel equal distance in equal time
and therefore reach the ground together in a vacuum.
9.
The
value of acceleration due to gravity on moon is 1.67m/s2. What does it mean?
The acceleration due to gravity on moon is 1.67m/s2. It means that the velocity of a freely falling body towards the
surface of moon increases at the rate of 1.67m/s in every second.
10.
Why
does the value of g is more in polar region than in the equator?
The value of g at a place is inversely proportional to the square
of the radius of the earth at that place. The radius of the earth at the poles
is lesser than the radius of equator. Therefore, the value of g is more
at the polar region (9.83m/s2) than equator
(9.78m/s2).
11.
Write
two differences between G & g.
|
Gravitational Constant (G) |
Acceleration due to gravity (g) |
|
1. Gravitational constant is the force of
gravitation between two bodies each with a mass of 1kg at a distance of
1meter apart. |
1. The acceleration developed in an object
falling freely without resistance towards the surface of the earth as a
result of gravity is called acceleration due to gravity. |
|
2. The value of G remains constant. |
2. The value of g channges from place to
place. |
|
3. It is a scalar quantity |
3. It is a vector quantity |
12.
The
weight of a body is more at the polar region than the equatorial region. Why?
13. The weight of a body at any place is directly
proportional to the acceleration due to gravity (g). The value of 'g' is
inversely proportional to the square of the radius of the earth. The radius of
the earth is less at the polar region than that of the equatorial region. So,
the weight of a body is more at the polar region than the equatorial region.
14. Why can't we fall safely with the help of
parachute towards the moon's surface?
15. We can't fall safely on the moon's surface with
the help of a parachute because there is no atmosphere, therefore there
is no upthrust due to air which reduces the velocity of falling parachute.
Thus, the parachute falls hardly and we get hurt while jumping with parachute
on moon's surface.
16. What change occur in the gravitational force
between two bodies when mass of each body is double and distance between their
centre is halved?
Let
us suppose two masses m1 and m2 are kept at a distance of d apart. The
gravitational force produced between them is:
Therefore, the gravitational force will increase by 16 times when the masses of two bodies are doubled and the distance between them is halved.
17. Under what condition the value of gravitational
force and gravitational constant become equal, prove.
When
the masses of each bodies are 1kg and the distance between them is 1m then the
value of gravitational force and gravitational constant become equal.
We know that
18.
What
is the value of acceleration due to gravity at the polar region? Write two
differences between free fall and weightlessness.
The value of acceleration due to gravity at the polar region is
9.83m/s2. Two differences between freefall and
weightlessness are:
|
Free fall |
Weightlessness |
|
1. It is the motion of
the body under the influence of gravity alo9ne. |
1. It is the condition
in which a body experiences that it is not being attracted by any force. |
|
2. It is possible in
absence of air. |
It is possible in a
freely falling body. |
19.
Why
is the weight of an object on the moon 1/6th its on the weight on the earth?
OR
The weight of a body is less on the surface of the moon than the
earth, why?
The mass of the moon is 1/100 times and its
radius ¼ times that of earth. As a result, the gravitational attraction on the
moon is about only one sixth when compared to the earth. Hence, the weight of
an object on the moon is 1/6th its weight on the earth.
20.
Write
two differences between gravity and gravitational force.
|
Gravity |
Gravitational force |
|
1. It is the force
with which a heavenly body such as earth pulls an object towards its centre. |
1. It is the force of
attraction between two heavenly bodies. |
|
2. It is a vector
quantity. |
It is a scalar
quantity. |
21.
A
stone and a piece of paper are dropped from the same height on the lunar
surface, which one will fall faster, why?
Both the stone and the piece of paper will fall simultaneously,
when they are dropped from the same height. This is because there is no
atmosphere on the moon and thus there is no resistance on the falling stone and
paper. Also, the acceleration due to gravity on both of them are equal.
22.
Acceleration
due to gravity vary from place to place on the earth, why?
The value of g is inversely proportional to the square of the
earth's radius. i.e. g∝1R2. The earth is not a
perfect sphere. That is, different parts on the earth's surface are at
different distance from the center of the earth. This means the value of R
(radius of earth) varies from place to place on the earth's surface. Therefore,
the value of g differs at various places of the earth.
23.
When
a feather and a coin are dropped towards the surface of the earth, do they
reach the ground together? If this experiment is done in moon, what difference
occurs? Write with reason.
When a feather and a coin are dropped towards
the surface of the earth, coin reaches the ground earlier than feather. This is
because the volume of coin is lesser than feather and its density is more than
the feather. The resistance of the air on coin is lesser than that of feather.
Due to the air resistance, the feather drops slowly whereas the coin falls
faster.
If this experiment is done on moon both the coin and feather falls
together. This is because there is no any air resistance in moon and the
acceleration due to gravity is equal on both the coin and feather.
24.
Why
will a sheet of paper fall slower than one that is crumpled into a ball?
When a sheet of paper is crumbled into a ball,
then its density increases. Hence, resistance to its motion through the air
decreases and it falls faster than the sheet of paper.
25.
Write
the main conclusion of Galileo's 'Feather and coin experiment'?
The main conclusion of Galileo's 'Feather and
coin experiment' is that in the absence of air resistance (in vacuum) all the
objects whether massive or minute falls together with the same acceleration due
to gravity. Fall of an object towards the surface of a heavenly body is
independent of the mass of the object.
26.
What
happens to the weight of an object when it is taken from the earth to the moon?
Why?
The weight of an object is reduced to 1/6 of its
weight on the moon. This is because the weight of a body is directly
proportional to the acceleration due to gravity and the value of acceleration
due to gravity is 1/6 times lesser than that of the earth.
27.
Why
do all planets and satellites revolve around the sun?
All planets and satellites revolve around the
sun because of the gravitational forces existing between them.
28.
Why
do satellites not fall while revolving around the earth?
During the revolution of the satellite around
the earth, the gravitational force of the earth and the satellite produces
necessary centripetal force while the inertia of the satellite provides
centrifugal force. These two forces balances each other. Hence, the satellites
do not fall while revolving around the earth.
29.
Why
does a sheet of paper falls later on the surface of the earth than the paper
ball of equal weight if throw from a certain height?
The sheet of a paper falls later on the surface
of the earth than the paper ball of equal weight if thrown from a certain
height. This is because a sheet of paper has larger surface area and hence
upthrust due to air on it is very high as compared to the paper ball of equal
weight. Due to this reason the sheet of paper falls later than the paper ball
of equal weight.
30.
A
satellite does not need any energy to revolve around the earth, why?
A satellite does not need any energy to revolve
around it because the energy required for the revolution around the earth is
provided by the balanced centripetal force by gravity and centrifugal force due
to inertia of motion of satellite.
31.
What
will be the acceleration due to gravity if the radius of the earth is
decreased? Why?
The acceleration due to gravity of the earth
will increase if its radius is decreased. This is because the value of
acceleration due to gravity is inversely proportional to the square of the
radius of the earth. i.e. g∝1R2.
Thus, if the radius is decreased the value of acceleration due to gravity
increases.
32.
Explain
on the basis of Newton's law of gravitation that the weight of an object
farther from the centre of the earth is lesser.
According to the law of gravitation, from the
formula W=GMm(R+h)2 weight of an object is inversely proportional to the square
of the distance from the centre of the earth. It means as the distance
increases there is decrease in the weight of an object. So weight of an object
farther from the centre of the earth is lesser.
33.
We
do not get hurt when we jump with a parachute, why?
When we jump with a parachute on the earth, the
upthrust of air act in upward direction and the weight of parachute in downward
direction. Upthrust due to air, thus reduces the velocity of the parachute and
hence it moves slowly under the action of gravity and hence we do not get hurt.
34.
The
probability of getting hurt is more when a man jumps from a significant height,
why?
Acceleration due to gravity produces on the
every falling body towards the earth's surface. When a body falls, there is
acceleration due to gravity. Due to acceleration, the velocity of body
increases and the force also increases. In this way, the probability of getting
hurt is more when jumps from significant height.
35.
What
is the difference between fall of a prachute on the earth and that on the moon?
On the earth parachute at fist falls with the acceleration same as
acceleration due to gravity i.e. free fall. But after certain time the upthrust
due to air and downward force by parachute balance each other. Due to the
balanced forces it attains a constant velocity and falls slowly. But there is
no atmosphere on the moon's surface, therefore the parachute falls down freely
due to the action of gravity alone.
36.
Give
two differences between mass and weight.
Two differences between mass and weight are:
|
Mass |
Weight |
|
1. It is the quantity
of matter contained in a body. |
1. It is the force of
gravity applied by the earth to pull any object towards its centre. |
|
2. It is constant. |
2. It is variable. |
|
3. Its SI unit is Kg |
3. Its SI unit is
Newton |
37.
What
are the two factors that effect the gravitational force?
The two factors that effect the gravitational force are: (i)
Masses of the two bodies and (ii) distance between them from their centres.
38.
At
what condition, does a coin and feather fall together? What is the acceleration
of the feather and coin at that instant? Justify your answer.
A coin and feather fall together in the vacuum or in the absence
of air. The acceleration of feather and the coin at that instant is equal to
the acceleration due to gravity. This is because the acceleration due to
gravity is independent of the mass of object.
39.
It
is difficult to lift a large stone on the earth but easier to lift the smaller
one. Why?
The weight of a body is directly proportional to the mass of a
body. A large stone has more mass than the smaller one. Hence, its weight is
more than the smaller one. So it is difficult to lift a large stone on the
earth than the smaller one.
40. Give reason, why
an iron ball and a feather fall together in vacuum.
Since the acceleration
due to gravity does not depends upon the mass of the body. There is no upthrust
or resistance in vacuum, so both an iron ball and feather fall with the same
acceleration.
41. The mass of the
earth is 6×1024kg. What is the value of acceleration due to gravity
of an object which is placed at a distance of 19200 km from the centre of
earth? (G= 6.67×10-11Nm2kg-2)
Given,
Mass of the earth (M) = 6×1024kg
Distance of object from centre of earth (R) = 19200
km = 19200×1000 m
= 1.92×107m
Gravitational constant (G) = 6.67×10-11Nm2kg-2
Acceleration due to gravity at 19200 km (g) = ?
We have formula,
42.
The
mass and the radius of the moon are 7.1×1022kg and 1.7×103km
respectively. Calculate the acceleration due to gravity on the moon's surface.
Given,
Mass of the moon (M) = 7.1×1022kg
Radius of the moon (R) = 1.7×103km = 1.7×106m
Gravitational constant (G) = 6.67×10-11Nm2kg-2
Acceleration due to gravity on the moon's surface
(g) = ?
43.
The mass of Venus and Sun are 4.89×1024
kg and 2×1030 kg respectively and distance between them 1.072×108
km. Find out the gravitational force between them. (Gravitational constant is
6.67×10-11Nm2kg2)
Solution,
Mass of Venus (m1) = 4.89×1024
kg
Mass of Sun (m2) = 2×1030kg
Distance between mass and sun (d) = 1.072×108
km = 1.072×1011 m
Gravitational constant (G ) = 6.67×10-11Nm2kg-2
Gravitational force (F) = ?
We know that,
44.
The mass and
the radius of Jupiter is 1.9×1027kg and 71×106m
respectively, find the acceleration due to gravity of it. What will be the
weight of an object having mass 75 kg on that planet?
Mass of the Jupiter (M) =1.9×1027kg
Radius of the Jupiter (R) = 71×106m
Gravitational constant (G) = 6.67×10-11Nm2kg-2
Mass of the object (m) = 75 kg
Acceleration due to gravity on the Jupiter's surface
(g) = ?
Weight of the object of mass 75 kg (W) = ?
We have,
45.
Mass of the earth is 6×1024kg and radius
is 6400km. What will be the weight of meteor having mass 1000kg at the height
of 10 km from the earth surface? Calculate.
Mass of the earth (M) = 6×1024kg
Radius of the earth (R) = 6400 km = 6.4×106m
Mass of the meteor (m) = 1000kg
Height of meteor from the surface of the earth (h) =
10 km = 1×104m
Gravitational constant (G) = 6.67×10-11Nm2kg-2
Weight of meteor at that height (W) = ?
We know that,
46. Write the correct expression for the force of gravitation that exits 'tween two stars having masses 'X' and 'y' respectively and separated by distance 'a'.
Here, Mass of the star (m1) =x
Mass
of the 2nd star (m2)=y
Distance
between them (d) ='a'
Gravitational
constant = G
Gravitational
force (F) =?
According
to Newton's law of gravitation,
47.
Group
C
1.
The
gravitational force produced between two bodies is 25N, when they are at the
distance of 4m apart. How much gravitational force is produced when they are
kept 2 m apart? Calculate.
Solution,
Let
the mass of the first body = m1
Let
the mass of the second body = m2
Distance
between them (d) = 4m
Force
at 4 m distance (F1) = 25N
Gravitational
constant (G) = 6.67×10-11N/m2
According
to the question,
or,
or,
25×16 = Gm1m2
or,
400 = Gm1m2.........................(i)
2.
If two bodies are kept at a distance of 400m, the
gravitational force between the bodies is 4.16875×104N. The mass of
one body is 2×107Kg, find the mass of another body. (G = 6.67×10-11Nm2kg2)
Solution,
Mass of First body (m1) = 2×107
kg
Distance between the bodies (d) = 400 m
Gravitational force (F) = 4.16875×104N
Gravitational constant (G ) = 6.67×10-11Nm2kg-2
Mass of Sun (m2) = ?
We know that,
3.
The mass of
jupiter is 319 times greater than that of the earth and its radius is 11 times
than that of the earth. If the acceleration due to gravity on the earth surface
is 9.8m/s2, find the acceleration due to gravity on the surface of
Jupiter.
Solution,
Let the mass of the Earth (Me) = M Kg
Then, mass of Jupiter (Mj) = M×319 Kg
Let the radius of earth (Re) = R
The radius of Jupiter = R×11 m
Acceleration due to gravity on the surface of earth
(ge) =9.8m/s2
Acceleration due to gravity on the surface of
Jupiter (gj) =?
According to the question,
Very
Long Answer Questions [4 marks each]
4.
On the basis of the figure given below, answer the
following questions.
(i) Keeping the masses constant if the
distance is halved (d/2). How many times does the gravitational force increase?
When
the distance is made half
(ii) Keeping the
distance constant and increasing the mass four times, what is the effect on the
gravitational force between A and B?
If
the mass increases 4 times at constant distance, then the gravitational force
between A and B also increases 4 times.
(iii) Keeping
the mass constant, what happen to the gravitational force if the distance
between the two bodies becomes doubled?
When
the distance is doubled (2d) by keeping masses constant, the
gravitational
force will be one forth
5.
In the given
figure, the two masses of m1 and m2 are separated at
distance 'd m1 and m2 are kept in air medium. Answer the
following questions.
(i) If water is
replaced by air in between these masses, what difference takes place in gravitational
force? Give reasons.
There
is no different in the gravitation of these two bodies because the value of
gravitational force does not depend on the medium between these mass (m1 and
m2).
(ii) Which law
of motion is related with the gravitational force between two masses (m1
and m2)? Give reasons.
The
gravitational force produced between the two masses follows the Newton's third
law of motion because the attraction force applied on each other is equal and
opposite.
6. Write and prove
Newton's Law of gravitation.
According
to the Newton’s law of gravitation, the force of gravitation between two bodies
is directly proportional to the Product of their masses and inversely
proportional to the square of the stance between their centers."
Consider two bodies having masses m1 and m2 are separated by the distance and the gravitational force between them is 'F'.
7. Calculate the
expression for gravitational force between two objects 'A' and 'B' as shown in
the figure.
Here,
Mass of object A = m1
Mass of object B = m2
Distance between them = d
Gravitational constant = G
Gravitational force produced between them (F) = ?
According to Newton's law of gravitation,
8.
Derive
OR
Prove that acceleration due to gravity is independent of the mass of a body.
The
force of gravitation between earth and object is in accordance of Newton’s law
of gravitation is:
According
to the Newton’s second law of motion, Force is the product of mass and
acceleration.
Here,
the acceleration is replaced by acceleration due to gravity ‘g’. Therefore,
Force between Earth and object is the product of mass of the object and acceleration
due to gravity i.e.
F=mg
……………………..(ii)
Putting
the value of F from equation (ii) in equation (i), we get,
|
g = |
In
the above equation, the value of G is universal constant, the value of M is
constant for a particular planet or heavenly body. Therefore the value of g
depends upon the value of R. So
The
value of R varies from place to place on earth or a heavenly body.
Thus, the value of acceleration due to gravity is inversely proportional to the square of radius of a heavenly body. So, g is independent of the mass of an object.
Some extra
questions
1. What Is
force? Write its unit of measurement.
Force is the push or pull factor on a body which
changes or tends to change the state of rest or of uniform motion in a straight
line. The SI unit of measurement of the force is called Newton (N). In CGS
system it can be measured by dyne.
[Force = mass x acceleration]
2. Define the gravity.
The force of attraction with which a planet (earth)
pulls an object towards its center is called gravity of the planet (earth). Its
SI unit is Newton.
The magnitude of force of attraction between any two
bodies in the universe is known as gravitational force.
4.Write down the three effects of gravity.
The three effects of gravity are as follows:
a) We can stay on the earth's
surface.
b) The reason behind the stability of
large buildings is also the gravity.
c) If there is no gravity, the river
will not flow, the atmosphere will not cover the earth's surface etc.
5. Give any two
evidence in support of the gravitation law.
Or, Write down
the two effects of gravitation.
a) It is the force of gravitational
attraction due to which earth orbits around the sun and the moon orbits around
the earth.
b) Due to the gravitational
attraction of the sun and the moon sea tides occur and are maximum on full moon
day.
c) Man has been able to go into space
only with he help of the Newton's law of gravitation.
6. Write any two differences between gravity and
gravitation.
The main differences between gravity and gravitation
are given below:
|
Gravity |
Gravitation |
|
(1) It is the force of attraction of
earth by which it pulls any objects towards its center. (2) Any object thrown up comes to the earth duetothe gravity. (3) The gravitymakesthe weight of the
object on the surface of the earth. |
(1) The force of attraction
between any (1) The force of attraction between any two massesin the universe is known as gravitation. (2) The stars and planets are
kept in their position due to the force of gravitation. (3) The gravitational force
collects the particles on the space together to form planets, moon etc. |
The gravitational force produced between two
heavenly bodies is directly proportional to the product of their masses and
inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
F α m1×m2 ................(i)
F α 1/d2......................(ii)
or, F = Gm1m2/d2
When two objects each having unit mass is separated
by unit distance, then gravitational constant G becomes equal to gravitational
force 'F'.
9. What is the
value of gravitational constant 'G'?
The value of gravitational constant 'G' is 6.67 x
10" Nm2/kg2
10. Find out the
SI unit of gravitational constant 'G' by applying gravitational formula From
Newton's Law of gravitation,
F =G
or, Fd2 =Gm1
m2
or, G m1 m2 = Fd2
or, G=Fd2 /m1 m2
In terms of SI unit:
Therefore, SI unit of G=Nm2/kg2
11. The stone
thrown upward in the sky returns back to the earth, Why?
The earth attracts every objects towards its centre
due to the one of gravity. Therefore, the stone thrown up the sky return back
to the earth.
12. Moon has no
atmosphere like earth, why?
The gravity of moon is not sufficient to hold
atmosphere around it's surface like that of the earth and hence moon has no
atmosphere.
13. An apple
falls from a tree on the earth. This is explained as a result of gravitational
force on it by the earth. Does the apple also attract the earth?
We know, gravitation is an interaction. Hence, force
on the apple by the earth must be equal and opposite of the force on the earth
by the apple.
14. What is the
reason behind arising of tides in the sea?
The arising of the tides in the sea is because of
the gravitational force between sun and moon.
15. The earth's
orbit is oval in shape. Explain how the magnitude of the gravitational force
between the earth and the Sun changes as the Earth moves from position 'A 'to
'B' as shown in the figure below.
In the given diagram, the distance
between the sun and the earth is less when the earth is located at the position
'A' than that in the position 'B'. According to Newton's law of gravitation,
the gravitational force between any two objects is inversely proportional to
the square of the distance between their centre. Therefore the magnitude of the
gravitational force between the sun and the earth is more when the earth is at
position 'A' than that in the position 'B'.
16. Why is
Newton's law of gravitation called universal law?
Newton's law of gravitational holds
true for all bodies whether terrestrial or celestial. That is, the force of
gravitation exists everywhere in the universe and for all bodies whether
microscopic or not. Therefore, it is called Universal law.
17.
You have a bag of cotton and an iron bar, each indicating a mass of 100Kg when
measured on a weighing machine. In reality, one is heavier than the other. Can
you say which one is heavier and why?
Ans: The cotton bag has larger
surface area than iron bar. The cotton bag experience larger up thrust of air
than its actual mass. So an iron bar is heavier than cotton bag, although both
have same mass.
18.
Gravitational forces acts on all objects in proportion to their masses. Why
then, a heavy object does not fall faster than a light object?
Ans: All objects fall on the ground
with constant acceleration, called acceleration due to gravity ( in the absence
of air resistance). It is constant and does not depend upon the mass of an
object. Hence, heavy objects do not fall faster than light objects.
19.
The earth and the moon are attracted to each other by gravitational force. Does
the earth attract the moon with a force that is greater or smaller or same as
the force with which the moon attracts the earth?
Ans: According to the universal law
of gravitation, two objects attract each other with equal force, but in
opposite directions. The earth attracts the moon with equal force with which
the moon attracts the earth.
20.
If the moon attracts the earth, why doesn't the earth move towards the moon?
Ans:
The earth and the moon experience
equal gravitational forces from each other, However, the mass of the earth is
much larger than the mass of the moon. Hence, it accelerates at a rate lesser
than the acceleration rate of the moon towards the earth. For this reason, the earth
does not move towards the moon.
21. Arpit buys a few grains of gold by weighing it
in spring balance at the poles. He hands over the same when he meets him at the
equator. Will the friend agree with the weight of gold bought? If not, why?
[Hint: The value of gis greater at the poles than at the equator].
Ans: Weight
of a body on the Earth is given by:
W= mg
Where,
m= Mass of the body
g= Acceleration due to gravity
The value of g is greater at poles than at the
equator. Therefore, gold at the equator weighs less than at the poles. Hence,
Arpit's friend will not agree with the weight of the gold bought.
22. Gravitational force on the surface of the moon
is only 1/6 as strong as gravitational force on the Earth. What is the weight
in newtons of a 10 kg object on the moon and on the Earth?
Ans: Weight
of an object on the moon = 1/6 x Weight of an object on the Earth
Also,
Weight = Mass x Acceleration
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.8 m/s2
Therefore, weight of a 10 kg object on the Earth =
10 x 9.8 = 98 N
And, weight of the same object on the moon= 1.6 x
9.8 = 16.3 N.
23. Calculate the force of
gravitation between the earth and the Sun, given that the mass of the earth = 6
× 1024 kg and of the Sun = 2 × 1030 kg. The average
distance between the two is 1.5 × 1011 m.
Ans: According to question,
Mass of the Sun (m1) = 2 × 1030 kg
Mass of the Earth (m2) = 6 × 1024 kg
Average distance between the Earth and the Sun (d) =
1.5 × 1011 m
From Universal law of gravitation,







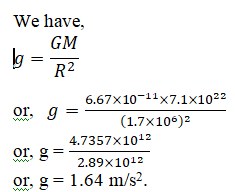














Post a Comment
Thank you for your comment