Lesson-2: Internet and Services
Introduction

The Internet is the worldwide "network of networks" that links millions of computers together via copper wires, fiber-optic cables, wireless connections, and other telecommunications channels. This publicly accessible network of interconnected computer networks communicate using a set of protocols and standards, the most basic of which are TCP/IP.
The Internet and the World Wide Web are everywhere. They can provide answers to questions and hours of entertainment. The Internet can allow people from all over the world to talk to each other. But what exactly are the Internet and the World Wide Web?
This resource is intended to function as a general overview of the workings of the Internet, which may cover social, economic, historical and other aspects. For a more detailed and step by step approach to learning about networking, consider visiting the topic on computer networking.
In 1961, Leonard Kleinrock wrote about ARPANET, the predecessor of the Internet, in a paper entitled "Information Flow in Large Communication Nets." Kleinrock, along with other innnovators such as J.C.R. Licklider, the first director of the Information Processing Technology Office (IPTO), provided the backbone for the ubiquitous stream of emails, media, Facebook postings and tweets that are now shared online every day. Here, then, is a brief history of the Internet:
The precursor to the Internet was jump started in the early days of computing history, in 1969 with the U.S. Defense Department's Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET). ARPA-funded researchers developed many of the protocols used for Internet communication today. This timeline offers a brief history of the Internet’s evolution:
1965: Two computers at MIT Lincoln Lab communicate with one another using packet-switching technology.
1968: Beranek and Newman, Inc. (BBN) unveils the final version of the Interface Message Processor (IMP) specifications. BBN wins ARPANET contract..
1969: On Oct. 29, UCLA’s Network Measurement Center, Stanford Research Institute (SRI), University of California-Santa Barbara and University of Utah install nodes. The first message is "LO," which was an attempt by student Charles Kline to "LOGIN" to the SRI computer from the university. However, the message was unable to be completed because the SRI system crashed.
1972: BBN’s Ray Tomlinson introduces network email. The Internetworking Working Group (INWG) forms to address need for establishing standard protocols.
1973: Global networking becomes a reality as the University College of London (England) and Royal Radar Establishment (Norway) connect to ARPANET. The term Internet is born.
1974: The first Internet Service Provider (ISP) is born with the introduction of a commercial version of ARPANET, known as Telenet.
1974: Vinton Cerf and Bob Kahn (the duo said by many to be the Fathers of the Internet) publish "A Protocol for Packet Network Interconnection," which details the design of TCP.
1981: The National Science Foundation (NSF) provided a grant to establish the Computer Science Network (CSNET) to provide networking services to university computer scientists.
1982: Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and Internet Protocol (IP), as the protocol suite, commonly known as TCP/IP, emerge as the protocol for ARPANET. This results in the fledgling definition of the Internet as connected TCP/IP internets. TCP/IP remains the standard protocol for the Internet.
1983: The Domain Name System (DNS) establishes the familiar .edu, .gov, .com, .mil, .org, .net, and .int system for naming websites. This is easier to remember than the previous designation for websites, such as 123.456.789.10.
1985: Symbolics.com, the website for Symbolics Computer Corp. in Massachusetts, becomes the first registered domain.
1986: The National Science Foundation’s NSFNET goes online to connected supercomputer centers at 56,000 bits per second — the speed of a typical dial-up computer modem. Over time the network speeds up and regional research and education networks, supported in part by NSF, are connected to the NSFNET backbone — effectively expanding the Internet throughout the United States. The NSFNET was essentially a network of networks that connected academic users along with the ARPANET.
1989: World.std.com becomes the first commercial provider of dial-up access to the Internet.
1990: Tim Berners-Lee, a scientist at CERN, the European Organization for Nuclear Research, develops HyperText Markup Language (HTML). This technology continues to have a large impact on how we navigate and view the Internet today.
1991: CERN introduces the World Wide Web to the public.
1992: The first audio and video are distributed over the Internet. The phrase "surfing the Internet" is popularized.
1993: The number of computers connected to NSFNET grows from 2,000 in 1985 to more than 2 million in 1993. The National Science Foundation leads an effort to outline a new Internet architecture that would support the burgeoning commercial use of the network.
1994: Netscape Communications is born. Microsoft creates a Web browser for Windows 95.
1994: Yahoo! is created by Jerry Yang and David Filo, two electrical engineering graduate students at Stanford University. The site was originally called "Jerry and David's Guide to the World Wide Web." The company was later incorporated in March
1995: Compuserve, America Online and Prodigy begin to provide Internet access. Amazon.com, Craigslist and eBay go live. The original NSFNET backbone is decommissioned as the Internet’s transformation to a commercial enterprise is largely completed.
1995: The first online dating site, Match.com, launches.
1996: The browser war, primarily between the two major players Microsoft and Netscape, heats up. CNET buys tv.com for $15,000.
1997: Netflix is founded by Reed Hastings and Marc Randolph as a company that sends users DVDs by mail.
1998: The Google search engine is born, changing the way users engage with the Internet.
2003: The SQL Slammer worm spread worldwide in just 10 minutes. Myspace, Skype and the Safari Web browser debut.
2005: YouTube.com launches. The social news site Reddit is also founded. 2004: Facebook goes online and the era of social networking begins. Mozilla unveils the Mozilla Firefox browser.
2006: Twitter launches. The company's founder, Jack Dorsey, sends out the very first tweet: "just setting up my twttr."
2010: Facebook reaches 400 million active users.
2013: Fifty-one percent of U.S. adults report that they bank online, according to a survey conducted by the Pew Research Center.
2015: Instagram, the photo-sharing site, reaches 400 million users, outpacing Twitter, which would go on to reach 316 million users by the middle of the same year.
2016: Google unveils Google Assistant, a voice-activated personal assistant program, marking the entry of the Internet giant into the "smart" computerized assistant marketplace. Google joins Amazon's Alexa, Siri from Apple, and Cortana from Microsoft.

Uses of Internet
INTERNET AND ITS USES : (SHORT ESSAY)
Internet is a global system that can be used for sharing information, providing worldwide services and communication. Daily updates are easily and instantly available in the internet. Also, you can search for any information you are looking for; in the internet. In today’s world, all companies are able to operate only with the use of internet. A lot of products and services are sold and provided through internet today. Once upon a time, telephone was considered a fast mode of communication. Now, internet has enormously emerged and replaced telephone as swift mode of communication.
INTERNET AND ITS USES : (BRIEF ESSAY)
The internet has intruded globally into everything than we could imagine. There are hardly people who do not rely on the internet for their daily life. Internet has emerged in such a way that we happen to use it to run our daily life in some way. The uses of Internet are endless; a few of them are as follows:
Education : Internet is a valuable source for a lot of information. Data and information related all fields are updated in the internet. Students can spend a few minutes over the internet to read their relevant study materials. Many students use internet for intense research on their projects.
Communication : With internet, communication has become better and easier. One can call and talk to someone over the internet. Video calls are an interesting option with communication through internet. Mailing is one another form of communication, which is widely used in daily corporate life.
Current Updates : Daily updates and current happenings are made available in the internet instantly. Internet is considered the real time hub for all updates about politics, sports, entertainment, science, business and many other fields.
Corporate Base : The corporate world relies on internet for file sharing, data transfer, internal communication and external communication; and many other purposes. In simple words, internet forms the base of the corporate today.
How does internet work?
Requirements for connection to the internet
Requirements for Internet Connection
1. Internet Connectivity
It is possible to confuse internet connection and internet connectivity. These are two different terminologies that we have broken down for you to understand better. Internet connectivity is a way or means of internet delivery.
There are several ways of internet delivery/ connectivity. For better understanding, we have explained some of these ways.
- Cable connectivity
This is the use of cables to deliver the internet from the source to the user. Cable internet is fast and reliable as it uses a broadband connection.
- Satellite connectivity
Satellite is another fast and reliable connectivity. Similar to cables, the satellite uses a broadband connection. However, they are different because unlike cables, the satellite uses an orbiting satellite dish to deliver the internet. Even it’s possible to get unlimited satellite internet using sattellite connectivity. Unfortunately, poor weather conditions like storms disrupt their internet delivery.
- Dial-up connectivity
Dial-up is the cheapest and slowest means of internet delivery. More often than not, dial-up delivers analog internet to landline phones for internet connection. Nevertheless, it uses modems to convert analog to digital signals to create internet connections in computers, tablets, and laptops.
- Wireless/ fiber connectivity
Fiber is a modern internet connection that uses wireless frequencies to deliver the internet to the user.
2. Internet service providers
ISPs are other essential requirements for the internet connection. I mean, an internet connection cannot be successful without service providers. This is because they are the source of the internet and its services. For a convenient internet connection, there must be an internet service provider in that specific area.
3. Connection devices
Connection devices like laptops, smartphones, desktops, watches, and tablets are also basic requirements for the internet connection. These devices are used to access the internet connection. In other words, internet connection cannot be complete without any of these devices.
A computer used during internet connection should have a strong system with a minimum processor of 486, minimum random access memory of 128 MB and a minimum hard disk of 40 GB.
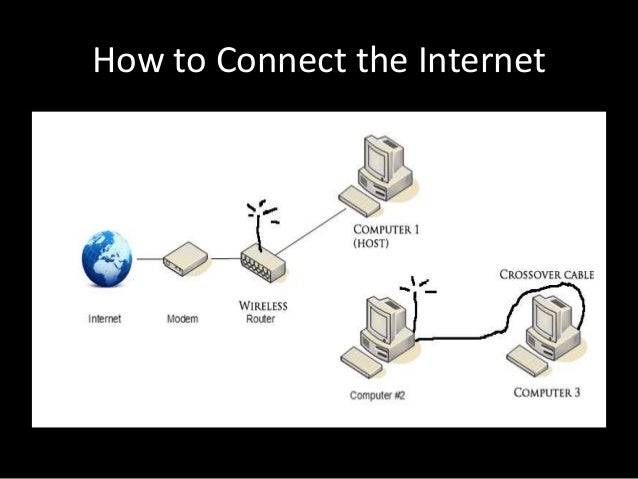
4. Hardware
Some computer hardware such as modems and routers are basic requirements for the internet connection.
Modem
Modems are the most preferred hardware during an internet connection. These devices have slots to insert your telephone line. Its major purpose is to pass an internet network from your telephone line to your computer. How? It does this by converting your telephone line analog signals to computer digital signals. Note that the reliability and convenience of modem connection depend on the types of computer, speed, and type of the modem.
There are several types of modems. These modems differ according to the type of internet connectivity. For instance; there is a telephone modem that is used for dial-up internet access, DSL modem for DSL internet access, cable modem for cable internet access and satellite modem for satellite internet access among others.
Router
A router is another essential hardware to the internet connection. Unlike modem, this device allows the user to connect several devices to a single internet at the same time, creating a WIFI. Through the use of a router, you can invent ways on how to get WIFI at home without cable.
Network interface card
This is another crucial hardware required during an internet connection. It can either be wired or wireless.
5. Software
A connection device cannot operate successfully without software. Some computer software plays a crucial role during internet connection. For instance;
Transmission control protocol software.
This is computer software that enables the transmission of data from one internet user to the other. It also guarantees the accuracy, privacy, and safety of data flowing in and out of a connection device/ computer.
Dialer software
Dialer software establishes an effective connection between the internet user and the server.
Web browser
The web browser is also a crucial requirement in internet connection. This software helps the user to use the internet to browse and search for needed information from a certain site.
Services provided by the internet
Services provided by the internet include:
1. Electronic Mail (e-mail)
2. World Wide Web
3. File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
4. Chat Rooms
5. Mailing list
6. Instant Messaging
7. News Groups
Electronic Mail
• Electronic mail, commonly known as email or e-mail, is a method of exchanging digital messages from an author to one or more recipients. Modern email operates across the Internet or other computer networks.
• Email servers accept, forward, deliver and store messages.
• An email message consists of three components, the message envelope, the message header, and the message body. The message header contains control information, including attachment option, reason box, email address and one or more recipient addresses. Message can consist of attachments, graphic or video/audio clips.
World Wide Web (WWW)
| Tim Berners-Lee Father of WWW, |
Search Engines
| Snap Shot of the Search Engine |
File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
- File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a standard network protocol used to transfer files from one host to another host over a TCP-based network, such as the Internet.
- FTP users may authenticate themselves using a clear-text sign-in protocol but can connect anonymously if the server is configured to allow it.
- The first FTP client applications were interactivecommand-line tools, implementing standard commands and syntax.
- Graphical user interface clients have since been developed for many of the popular desktop operating systems in use today.
Chat Rooms
Mailing List
Instant Messaging
News Groups
Video Conference:
A video conference is a live, visual connection between two or more people residing in separate locations for the purpose of communication. At its simplest, video conferencing provides transmission of static images and text between two locations. At its most sophisticated, it provides transmission of full-motion video images and high-quality audio between multiple locations.
In the business world, desktop video conferencing is a core component of unified communications applications and web conferencing services, while cloud-based virtual meeting room services enable organizations to deploy video conferencing with minimal infrastructure investment.

إرسال تعليق
Thank you for your comment